Régulièrement, cette rubrique animée par Virginia Allum, auteur et consultante EMP (English for Medical Purposes), vous permettra, exercices à l'appui, de parfaire votre anglais médical au travers de situations de soins concrètes. Ce cours est consacré à l'immunothérapie contre le cancer. Bon travail à tous ! Corrections en fin d'article...
N'hésitez pas à vous servir du dictionnaire en ligne Wordreference. Vous trouverez à la fin de cet article les corrections des exercices qui vous sont proposés téléchargeables au format pdf.
Before you start, think about the following :
- What cancer treatments do you know about?
- What do you know about the immune system of the body?
Exercise 1
Vocabulary
- cancerous
- immature
- immunity
- immunology
- innate
- innate lymphoid cell (ILC)
- lymph
- lymphatic tissue
- lymphocytes
- lymphoid
- B-cell
- T-cells
- Natural killer cell
- pathogen
- spongycadre
Complete the information about the immune system. Select the terms from the Vocabulary List.
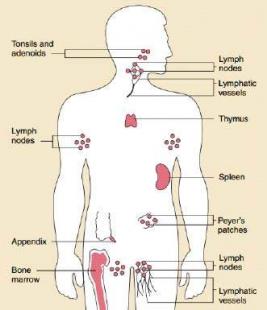
The immune system is formed of several structures called lymphoid organs in the body. A healthy immune system works to identify threats to the body from viruses, bacteria and other
(1) ________________ as well as cancer cells. It is the role of the immune system to keep them out or destroy them, if they manage to infiltrate a healthy cell.
- The primary lymphoid organs include :
- Bone marrow : The yellow, (2) _____________ tissue in the centre of bones produces white blood cells, for example T lymphocytes. Lymphocytes are immature cells, which become activated after contact with an antigen and grow into specific immune cell types, such as :
- T cells - to destroy infected or (3) _______________ cells ;
- B cells - to produce antibodies which attack bacteria, viruses and toxins ;
- Natural killer cells (NK cells) – contain a chemical which targets pathogens and cancer cells.
- Thymus : a small organ behind the sternum where (4) _____________ mature. T-cells move throughout the body, scanning the surface of cells for changes.
- Bone marrow : The yellow, (2) _____________ tissue in the centre of bones produces white blood cells, for example T lymphocytes. Lymphocytes are immature cells, which become activated after contact with an antigen and grow into specific immune cell types, such as :
- Secondary lymphoid glands include :
- Lymph nodes : include bone marrow, spleen, thymus and lymph nodes and contain (5) _______, a clear fluid which transports immune cells to different parts of the body. When the body is fighting infection, lymph nodes can become enlarged and feel sore.
- Spleen : largest lymphatic organ in the body which stores up to a quarter of (6) ___________ at any one time in the white pulp region. Lymphocytes are needed to fight infection and disease. The white pulp region is separated from the connective tissue of the red pulp region whose role is to help control the blood volume in the body and dispose of old or damaged blood cells.
- Tonsils : or palatine tonsils are small lumps of (7) ______________ tissue which form a ring on either side of the throat. The adenoids or pharyngeal tonsils are located at the back of the throat and into the nasal cavity The tonsils and adenoids entrap pathogens entering the mouth or nose.
- The body also contains other areas of lymphatic tissue, e.g. :
- Peyer’s Patches – small masses of (8) _______________ tissue in the small intestine which monitor the level of bacteria in the intestines.
- Appendix – contain (9) _______________ lymphoid cells (ILCs) which may restore ‘helpful’ bacteria in the gut, e.g. after a bacterial intestinal infection like food poisoning. Mucosal (10) _____________________ is the study of this type of immune response leading to the development of vaccines for diseases and conditions such as AIDS, influenza and food poisoning.
Exercise 2
Match the correct meanings
| 1. lymph | a. type of connective tissue containing lymphocytes |
| 2. lymphoid | b. something present from birth |
| 3. lymphatic tissue | c. resistant to disease |
| 4. lymphocyte | d. study of the immune system |
| 5. lymph node | e. type of white blood cell important for the immune response |
| 6. immune | f. clear fluid which carries lymph cells around the body |
| 7. immunology | g. mass of lymphoid tissue found along a lymphatic vessel |
| 8. innate | h. something which resembles lymph or relates to lymphatic tissue |
Exercise 3
Scan the text below and decide on the most appropriate title for the article.
- a) Drug Therapy for Bladder Cancer
- b) Immunology Therapy for Cancer Treatment
- c) Chemotherapy versus Radiotherapy for Cancer Treatment
- d) New Cancer Treatment: Monoclonal Antibodies
Text :
Immunotherapy is a type of biological therapy which uses substances from the body’s immune system to treat cancer.
Some of the types of immunology include :
1) Monoclonal antibodies (the ‘mabs’) – drugs which attach to specific targets in the body and provoke an immune response by acting as markers, so cancerous cells become visible to the immune system or by "releasing the brakes" on the immune checkpoints of the immune system so cancer cells can be destroyed.
Monoclonal antibodies which block these pathways are called immune checkpoint inhibitors. Examples of immune checkpoint inhibitors :
- Ipilimumab (Yervoy)
- Nivolumab (Opdivo)
- Pembrolizumab (Keytruda).
2) Adoptive Cell Transfer – treatment which boosts the ability of T-cells to fight cancerous cells. T-cells are removed from the tumour, modified in the lab and grown in large numbers before being returned to the patient’s body. Once there, they seek out and destroy cancer cells. This type of therapy is called chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy.
3) Cytokines – small signalling proteins which activate the T-cells fully after being injected into the body. Examples of these are Interferon α and Interleukin 2. Interferons help the immune system fight cancer and may slow the growth of cancer cells. Interleukins help the immune system produce cells that destroy cancer.
4) Treatment Vaccines - which work against cancer by boosting your immune system’s response to cancer cells. Treatment vaccines are different from the ones used to help prevent disease.
5) BCG – the use of the weakened form of the bacteria that causes tuberculosis. When inserted directly into the bladder via a catheter, BCG causes an immune response against the cancer cells which cause bladder cancer.
6) Oncolytic Virus Therapy - uses genetically modified viruses to kill cancer cells by injecting them directly into the tumour. After entering the tumour, the virus makes copies of itself causing cancerous cells to burst and die. As the cells die, they release new infectious particles which trigger the immune system to help destroy the remaining tumour. An example of this type of therapy is called the T-VEC virus.
Exercise 4
Complete the definitions using terms in the box below.
- limit
- tumour
- increase
- single
- infection
- change
- monoclonal – clone made of a ___________ cell
- oncolytic – something which absorbs or destroys a ______________.
- modify –____________ the structure of something
- boost –____________ the effect of something
- infectious – something which causes an _____________
- inhibit – block or ____________the function of something
Exercise 5
Answer the questions True /False about the text.
- Monoclonal antibodies may be used to mark out a tumour, so cancer cells can be destroyed.
True / False
- The drug ‘Pembrolizumab’ is an example of an immune checkpoint pathway, which leads from a monoclonal antibody to a cancerous cell.
True /False
- CAR T-cell therapy helps the body to fight cancerous cells by boosting its own T-cells.
True / False
- Interferons and Interleukins are types of immune T-cell proteins.
True / False
- The same vaccines can be used to prevent diseases like childhood illnesses as well as killing certain cancer cells.
True /False
- A weak form of the Bacillus Calmette-Guérin vaccine is now being used to treat bladder cancer.
True /False
- The term ‘oncolytic’ comes from onco- (cancer) and -lytic (break down).
True / False
- Oncolytic viruses select a particular cancer and mark it out for destruction by the immune system.
True /False
Téléchargez les corrections au format PDF
Virginia ALLUM Author and Consultant in English for Medical Purposes United Kingdom


REFONTE DE LA FORMATION
L'idée d'un tronc commun en master hérisse les infirmiers spécialisés
ÉTUDES
D’infirmier à médecin : pourquoi et comment ils ont franchi le pas
VIE ÉTUDIANTE
FNESI'GAME : l'appli qui aide les étudiants infirmiers à réviser
PRÉVENTION
Des ateliers pour préserver la santé des étudiants en santé